Research
Discover Solana, a high-performance Layer 1 decentralized applications chain using dual consensus mechanism for higher and cost effective transaction costs.
This Solana blockchain presentation goes beneath the surface to unravel how the network works, its use cases, its native token, SOL, Solana staking, and the network's contributions to the blockchain space.
What is Solana?
Solana is a high-performance Layer 1 blockchain for high throughput at near-zero transaction costs. The network leverages Delegated Proof-of-Stake (DPoS) and Proof-of-History (PoH) consensus mechanisms to process transactions efficiently. Its scalability makes a compelling argument for the mainstream adoption of blockchain technology.
While Solana focuses on speed and scalability, it shares similarities with Celestia blockchain's modular architecture for scalability.
The network can accommodate various decentralized applications, including NFTs, decentralized exchanges (DEXs), gaming applications, decentralized lotteries, and lending apps. Solana supports wrapped assets and stablecoins as well.
Like Ronin Network, Solana plays a key role in the NFT ecosystem, offering fast and cost-effective infrastructure for digital transactions
Wrapped assets are tokens designed to represent a cryptocurrency, say Bitcoin, on another blockchain network. Creating such a token involves wrapping the original asset with a smart contract, which issues the equivalent of the token in question on the desired blockchain.
The Solana Program Library (SPL) also supports the creation of other tokens on its mainnet.
The Premise of Solana Network
Unveiling blockchain technology raised hopes that it would shift how various segments of the global economy operated.
However, as soon as onboarding increased, it became clear that the tech stack, as originally constituted, could not manage enterprise use and mainstream adoption.
Challenges in early blockchain adoption
Scalability affected the first generation of Layer 1 blockchain networks, such as Bitcoin and Ethereum. Their architecture does not factor in the role of time in determining the speed of transactions despite timestamping being an integral component of blockchain operations.
As a result, the two blockchains are slow, considerably expensive, and consume vast amounts of energy.
Solana Network provides efficient solutions
Solana Network tackles these challenges. It processes thousands of transactions per second at under $0.01 and consumes less energy. Technically, the benchmark throughput of the Solana network is 65,000 transactions per second. This figure is based on simple tasks such as transferring value from one point to another.
Stake Solana with Imperator.co!
Maximize your SOL staking rewards : earn more, start now.
How does Solana work?
Solana network is a decentralized computing platform designed for scalability. To achieve this mission, it applies numerous novel approaches. A key factor among these is dual consensus, which involves employing PoS and PoH in transaction processing and finalization.
This approach leverages validators who secure the network by validating blockchain transactions and generating transaction sequences before including the data in the blockchain.
PoH, on the other hand, automates blockchain transaction ordering, delivering fast transaction speeds and settlement times. It is a more efficient transaction timestamping system that enables Solana Network to process thousands of transactions per second.
Architecture of the Solana Chain
The Solana network integrates several advanced features that enhance its speed, scalability, and overall efficiency.
Proof of History (PoH)
This consensus method adds the element of time to a blockchain ledger, providing a verifiable record of time that does not rely on a central clock and still preserves decentralization.
It cryptographically verifies the passage of time between events and chains the data from nodes about the validity of blocks, complete with a reference detail of the chronological order of creation.
Tower BFT
This is an iteration of the Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance technology that uses Solana’s PoH as a clock before consensus, an approach that reduces messaging overhead and latency.
Turbine
A multi-layer block propagation protocol that facilitates easier communication between nodes. Turbine leverages User Datagram Protocol (UDP) to shred blocks into data packets, making it easy to broadcast them across the network.
Gulf Stream
Regular blockchains rely on mempools to save data from unverified transactions. Solana uses Gulf Stream, a mempool-less forwarding protocol. This feature hastens transactions by ensuring applications do not hoard data about pending transactions.
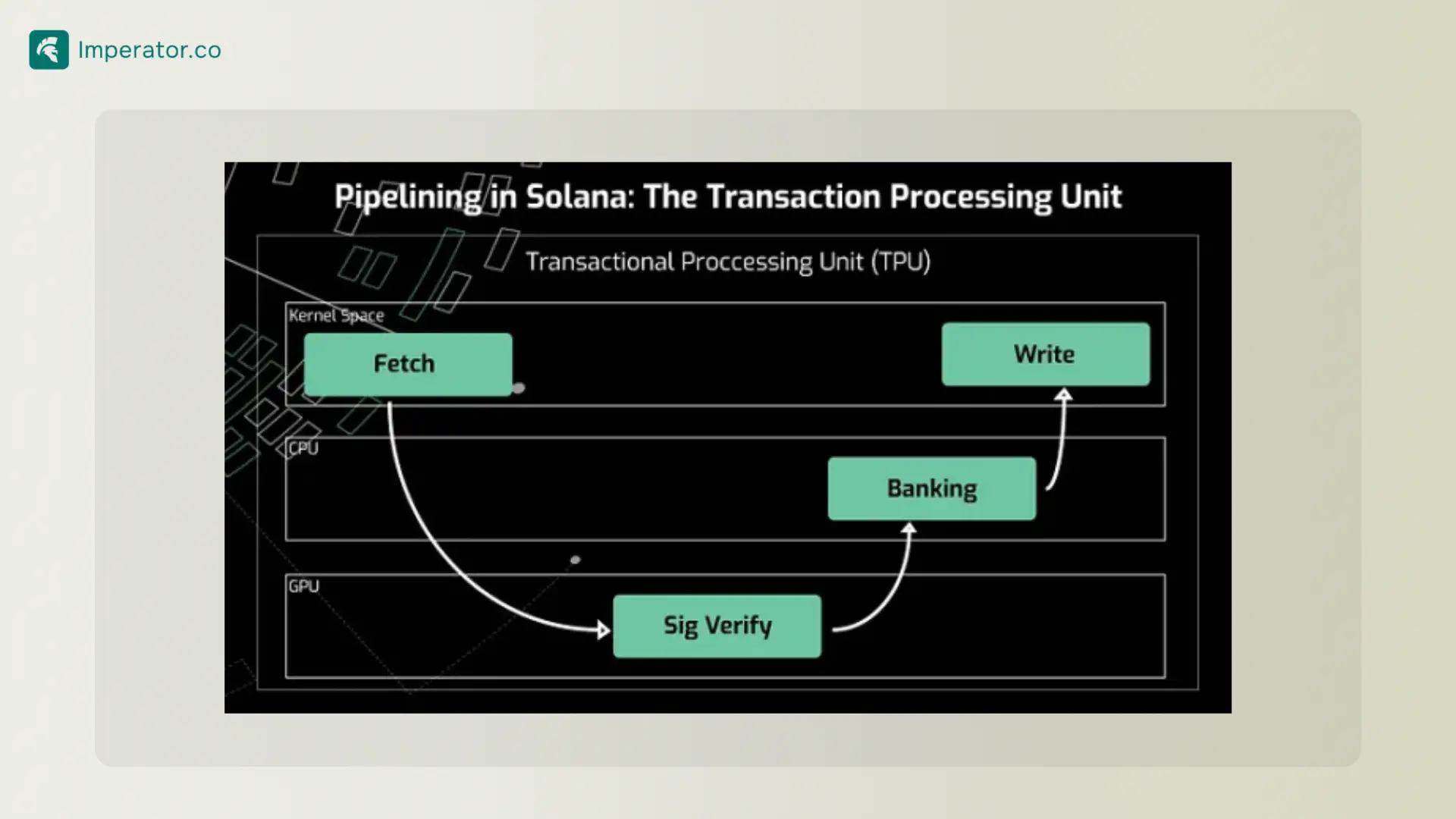
Pipelining
A rendering technology that optimizes the transaction life cycle. It initiates the execution process of incoming transactions before finalizing earlier transactions, boosting efficiency.
Ledger Archivers
Powers dApps on Solana by storing large volumes of network data efficiently. The feature leverages public symmetric keys for data encryption, ensuring that the data sequence remains accurate and verification of all proofs happens in a single take.
Sealevel
A smart contracts runtime that can process up to 65,000 contracts in parallel by optimizing validator core output.
Cloudbreak
A horizontally scaled accounts database that enables Solana to scale by morphing network participation into small parallel chains that increase the network’s overall processing capacity.
What Makes Solana Network Useful?
Solana was developed to address challenges plaguing first-generation blockchain networks. It puts forth four key breakthroughs:
Scalability — The chain’s architecture integrates native scalability, enabling it to process thousands of transactions and accommodate many users.
Throughput — It is among the very fast blockchains with a processing capacity of 65,000 TPS.
Energy conservation — The dual consensus technology consumes less energy than previous consensus mechanism modes.
Lower transaction costs — Solana processes transactions at a fraction of a penny, an important step toward the mass adoption of blockchain technology.
Who Created Solana Blockchain?
Solana was created in 2017 by Anatoly Yakovenko, Raj Gokal, Greg Fitzgerald, Eric Williams, Stephen Akridge, and Alan Yu. Anatoly, a former Qualcomm executive, introduced the Proof-of-History consensus. Raj, the COO, has expertise in business development, having founded startups like Sano.
Greg and Stephen are experienced software architects, while Eric, a particle physicist, led data science. Alan, now an advisor, contributed business insights.
Solana Labs develops tools, and the Solana Foundation oversees decentralization. The project raised over $350 million from investors like Andreessen Horowitz and Polychain Capital.
Role of SOL in Solana's Ecosystem
SOL is the native token of the Solana blockchain. It is used to pay transaction fees on the network and is the gas that facilitates the execution of transactions and smart contracts. Users get access to the services on the chain, such as DEXs and in-game items on the platform, using SOL tokens.
SOL also plays a critical role in securing the network. Validators stake their token to participate in validating transactions, generate PoH sequences, and create new blocks on the network. In return, they earn staking rewards.
SOL empowers holders to participate in the governance of Solana. Holders get to vote on decisions affecting the future of the chain.
The token can be used to transfer value because it can be sent from one user to another as payment. Solana Pay, the open, free-to-use payments application, allows users to transfer value among themselves.
How to get started with Solana
Follow these steps to get started on Solana:
Create a Wallet
Users require a SOL-compatible wallet to store and manage their tokens. Various platforms, including self-custody wallets, centralized exchanges, decentralized exchanges, and institutional custodians support the token.
Users should research extensively and settle on a suitable wallet. Note that self-custody wallets are ideal for long-term cryptocurrency holding.
Buy SOL Tokens
Follow the steps below to buy SOL tokens:
Sign up or log into an exchange.
Search for SOL tokens and buy using approved payment methods.
Transfer the tokens to a SOL-compatible wallet.
Use appropriately.
Staking SOL Tokens
Token holders who stake SOL earn rewards in exchange for facilitating the transaction validation, creating platform stability, and securing the Solana Network.





Discover all our Staking Opportunities
Acces over 50+ protocols to maximize your staking returns
We’ve written a comprehensive guide on the best Solana validators, detailing top choices for a secure and optimized staking experience
What is Solana: Closing thoughts
Solana has solidified its position as a high-performance blockchain, offering fast & low-cost transactions with minimal energy consumption. By combining Proof of History (PoH) and Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS), it addresses key scalability challenges faced by earlier networks.
With its continued innovation and ability to support a wide range of decentralized applications, Solana is set to remain a key player in the future of blockchain technology.
FAQs
What is Solana (SOL)?
Solana is a high-performance Layer 1 blockchain for high throughput and cost-effective transaction costs. SOL is the native token of the Solana blockchain used to pay for transactions on the network, staking to secure the platform, empower holders to participate in network governance, and earn staking rewards.
How does the Proof-of-History (PoH) consensus work on Solana?
Proof-of-History is a timestamping system that cryptographically verifies the passage of time between events. This improves transaction processing speed by avoiding the need for continuous synchronization of node clocks.
Why is Solana considered a high-throughput blockchain?
Solana is designed to process up to 65,000 transactions per second (TPS) thanks to its unique architecture, which includes protocols like Turbine, Sealevel, and Gulf Stream that optimize node communication and transaction management.
What is the SOL token and what are its uses?
SOL is the native token of Solana. It is used to pay transaction fees, secure the network through staking, participate in blockchain governance, and make payments via Solana Pay.
Who created the Solana blockchain?
Solana was created in 2017 by Anatoly Yakovenko, along with Raj Gokal, Greg Fitzgerald, Eric Williams, Stephen Akridge, and Alan Yu. Anatoly, a former Qualcomm executive, introduced the Proof-of-History consensus mechanism to enhance blockchain scalability.
What are the tokenomics of Solana?
The total supply of SOL is capped at 489 million tokens, with around 370 million currently in circulation. SOL tokens are used for transaction fees, staking rewards, and governance. The tokenomics are designed to encourage staking and long-term network participation, with rewards distributed to validators and stakers.
Maximize your SOL staking rewards : earn more, start now.






